Passive roaming LoRaWAN® packets
This topic describes reference information about passive roaming LoRaWAN® packets.
Passive roaming
Passive roaming is a mode by which a device can seamlessly roam away from home and uses base stations of the visited network --- connected to a forwarding network server (fNS) --- to reach its home network.
The following terminology is used in passive roaming mode:
-
A serving network server (sNS) or home network server (hNS) is where the device is provisioned. sNS manages the interface with the device's application server.
-
A forwarding network server (fNS) is an intermediate network server used as a bridge between the device and the serving network server. It forwards the LoRaWAN® packets between the device and the sNS when the device roams in a zone covered by the base stations of the visited network.
-
The serving and visited networks must have a roaming agreement in place.
The device's Over-The-Air activation mode is visible on the sNS, both from the network partner's and subscriber's Wireless Logger interfaces:
-
On the visited network (fNS) LoRaWAN® packets of roaming devices are displayed on the Wireless Logger attached to the network partner on the fNS. This allows the network partner of the visited network to monitor all the traffic routed through its base stations, including roaming traffic.
-
On the home network (sNS)
-
LoRaWAN® uplink/downlink packets are displayed on the Wireless Logger attached to the subscriber of the sNS. This allows the subscriber to monitor all the LoRaWAN® traffic of their devices whatever they are at home or roaming on other networks.
-
If an uplink packet is received by both fNS and sNS, then the packet is displayed on the Wireless Logger attached to the network partner on the sNs, only if the best-LRR (having the highest uplink SNR among all the receiving base stations) belongs to the sNS.
-
Passive roaming packets
There are two categories of passive roaming packets:
-
Forwarding passive roaming: The network server acts as a forwarding network server (fNS).
-
Serving passive roaming The network server acts as a serving network server (sNS).
To see all types of passive roaming packets, see LoRaWAN® traffic overview.
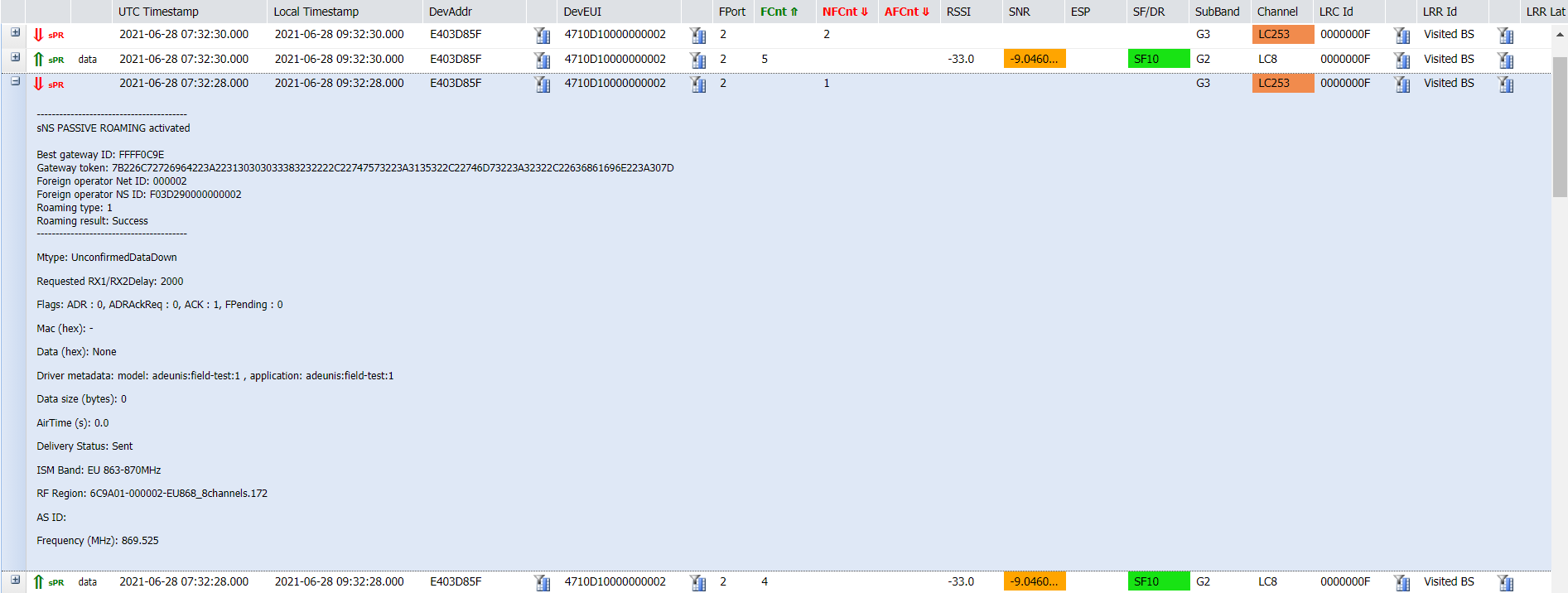
Passive roaming metadata
-
For uplinks, see Uplink metadata columns and Uplink expandable panel.
-
For downlinks, see Downlink metadata columns and Downlink expandable panel.