Checking the radio traffic history of the base station
-
Select Base Stations.
-
On the List tab, click the name of the base station for which you want to check the radio traffic.
-
In the Basic View tab or in the RF Statistics tab, go to RADIO TRAFFIC HISTORY.
-> The RF traffic information appears as follows:
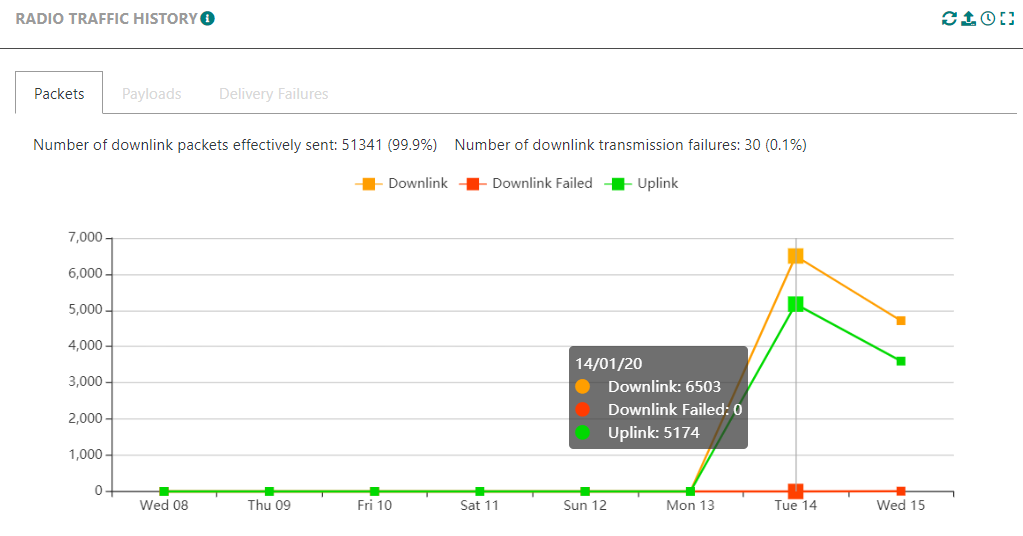
In the example, you can view the distribution of the network activity of a base station for a given time.
-
Click the Payloads tab to check payload sizes. -> The payload graph appears as follows:

-
Click the Delivery Failures to check the causes of the downlink transmission failures and their distribution.
-> A similar delivery failures' graph appears as follows:

-
Three types of pies show the distribution of the downlink transmission failures on the receive window. They are given for each device Class.
Pie type Explanation RX1 pie chart (All Classes) Failures on RX1 slot window. RX2 pie chart (All Classes) Failures on RX2 slot window. Ping slot pie chart (Class B specific) Failures on ping slot window. -
The downlink transmission may fail in five cases. They are given for each device Class.
Cause type Explanation Transmission slot busy Base station failed to send downlink because radio is not available: radio stopped, collision with another downlink transmission. Too late The downlink frame reached the base station too late for requested transmission slot, probably due to backhaul latency between base station and Network Server. Network Server selected RX2 (All Classes) Network Server decided to transmit the downlink on RX2 slot, either due to duty cycle constraints or for traffic optimization purposes. DC or base station constraint Transmission canceled to comply with legal usage of the sub-band (duty cycle or dwell time) or because no base station is available. Frame expired before transmission (All Classes) Base station was unable to transmit the downlink after the maximum retry period (only for class C devices). If you get one of the preceding results, you need to do the following for each situation: -
If you get one of the preceding results, you need to do the following for each situation:
Cause type Action to take Transmission slot busy See possible root causes and actions related to BS alarm 105 in Base station alarms. Too late Check the latency of the backhaul interface between the base station and the ThingPark core network. Network Server selected RX2 Not applicable DC or base station constraint If the BS supports Listen before Talk "LBT", check the background interference level through "Spectrum Analysis" utility. In case the noise level is too high (higher than -85 dBm), check if cleaner RF channels can be allocated to the base station. If the BS does not support LBT, excessive downlink duty cycle means that the base station has reached its downlink radio capacity; hence it is recommended to add new base stations to extend radio capacity. Frame expired before transmission Specific to class C downlink: the BS tries to send a class C downlink during max 60 seconds. If this maximum duration is reached, the transmission is canceled and the failure cause E0 is reported.