Application design
The application design can be represented as follows:
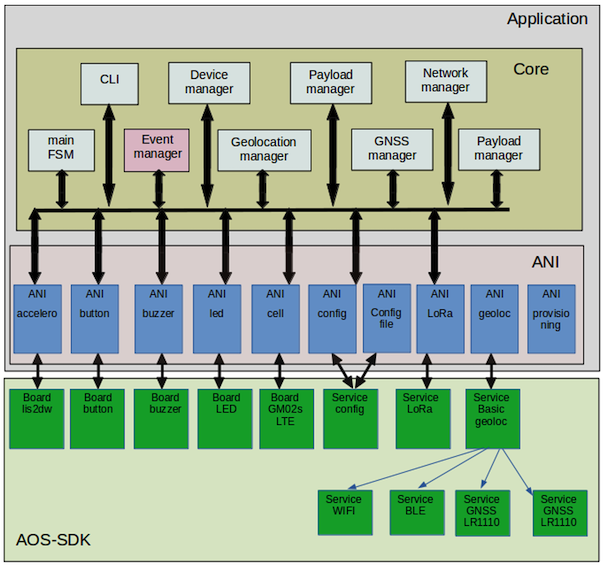
The application is structured into two main layers:
-
ANI (Application Node Interface)
The ANI layer provides the link between the application and the underlying service.- It usually controls a single service.
- It registers against the associated service callback and translates service events into application events.
- An ANI can also register with the event manager to capture specific events and trigger actions related to the service it manages.
-
Core
The core is the central part of the application. It includes:- A main FSM (Finite State Machine) that manages the system states (off, running, hold, etc.).
- An event manager that distributes application events to registered clients.
- A geolocation manager that schedules position acquisitions.
- A GNSS manager that manages almanacs and aiding positions.
- A network manager that handles networking using LoRaWAN and LTE.
- A payload manager that generates unsolicited uplinks (position, notifications).
- A device manager that monitors system health (temperature, battery level, etc.).
- A Command Line Interface (CLI) that allows system configuration and monitoring.
The application runs in a single thread (a FreeRTOS task).
- All application events are handled within this thread.
- Actions taken by the application are always executed under the application thread.
This mechanism enforces the synchronization required for a stable application in a multi-threaded system.