Downlink LoRaWAN® unicast packets
This topic describes reference information about downlink LoRaWAN® unicast packets.
Downlink packets
Downlink unicast packets are LoRaWAN® packets sent by base stations to a single device, either directly or via a LoRaWAN® relay. They are represented in Wireless Logger by purple icons:
illustrates a regular downlink unicast packet
illustrates the case of a downlink unicast packet sent in response to a repeated uplink packet that is invisible in Wireless Logger (due to packet deduplication). To learn more, see Downlinks generated for a repeated uplink.
illustrates the case of a downlink unicast packet sent in the context of a passive roaming agreement with a peer LoRaWAN® network (
Rstands for Roaming). To learn more, see Passive Roaming packets.illustrates the case of a downlink unicast packet forwarded to the device via a LoRaWAN relay.
Fstands for "Forwarded". To learn more, see Using LoRaWAN relays.
In case of transmission failure, that is the downlink packet could not be successfully transmitted by the base station over the air, a red dot displays on the icon.
- Example:
,
or
.
- The detailed delivery failure cause is shown in the expandable panel.
- To learn more, see Downlink delivery failure causes.
You can see and filter several categories of downlink packets in Wireless Logger according to their content. A frame is a packet.
| Downlink packet | Content | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MAC frames | When a downlink packet is tagged mac only, it means that the packet does not contain any applicative payload from the application server. These packets are either downlink packets carrying only Layer-2 LoRaWAN® MAC commands and/or MAC acknowledgements to a previous uplink confirmed packets. | |
| Data frames | These packets contain an applicative payload that is generated by application servers but do not contain any MAC commands. | |
| MAC + Data frames | These downlink packets contain both MAC commands/acknowledgments and applicative payload. | |
| Join Accept frames | These downlink packets are only relevant for OTA devices. |
Downlinks generated for a repeated uplink
When the same uplink packet is transmitted several times by the device (i.e. frame repetition), only one copy of this uplink packet is visible in Wireless Logger and sent to application servers thanks to the LRC deduplication mechanism.
However, since each individual uplink transmission by the device allows two downlink scheduling slots (RX1 and RX2), the LRC can send downlink packets on RX1 or RX2 slots of a repeated uplink packet.
To avoid any ambiguity:
-
Downlinks for a repeated uplink notifies that the downlink packet in question is sent in response to an uplink packet that is masked by deduplication.
-
In the expandable panel, LoRaWAN® MType is appended by (generated for a repeated UL).
Downlink delivery failure causes
For every downlink transmission from the network towards the device, Wireless Logger displays the following information in the expandable panel:
-
Downlink status, with two possible values:
-
Sent: If the downlink packet was successfully transmitted by the LRR base station.
In the example of the screenshot above, while the delivery status is Sent, Wireless Logger displays a failure cause on RX1 because the downlink packet was sent on RX2 instead of RX1. In this specific case, the RX2 choice is driven by the LRC RX1/RX2 selection algorithm (also known as RX2 Optimization).
noteSuccessful transmission by the base station does not guarantee successful reception by the device as the downlink packet might be lost over the air (due to collision for instance, or bad radio frequency coverage).
-
Failed: If the downlink packet could not be sent by the LRR base station. In this case, the delivery failure cause on RX1 and RX2 (and pingslot for class B devices) is indicated by Wireless Logger as illustrated by the following example for class A device:
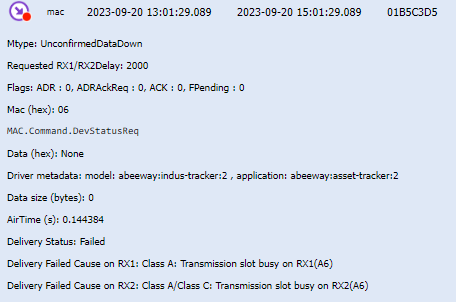
-
-
Delivery Failed Cause on RX1, RX2 and Pingslots.
Reminder Downlink packets can be scheduled over RX1 and class-A-RX2 slots for all the device classes (A/B/C). They can be additionally scheduled on the extended RX2 window for class C devices and the pingslots of class B devices.
The following table details the different delivery failure causes on RX1/RX2/Pingslots, for both unicast and multicast downlinks:
| Cause value | Category name |
|---|---|
| Over-the-air delivery error causes for RX1 downlink slot (all device classes) | Transmission slot busy on RX1 - (A0) Radio stopped - (A1) Downlink radio stopped - (A3) Radio busy - (A4) Listen before talk - (A5) Radio board error - (A6) Specific failure cause for Semtech basics station packet forwarder Received too late for RX1 - (B0) Too late for RX1 LRC selects RX2 - (C0) LRC selected RX2 Duty Cycle (DC) or gateway constraint on RX1 - (D0) >Duty cycle constraint detected by LRR - (DA) Duty cycle constraint detected by LRC - (DB) Max dwell time constraint detected by the LRC - (DE) DC not allowed by the peering operator (only applicable for passive roaming traffic) - (DF) Wrong NetID (i.e. device's NetID does not match the NetID associated with any eligible base station) Frame discarded from the downlink queue - (E1) Queue full - (E2) Invalid FCntDn - (E3) Validity time expired - (E4) Queue reset following a rejoin (i.e. queued packets are discarded) |
| Over-the-air delivery error causes for RX2 downlink slot (all device classes) | Transmission slot busy on RX2 - (A0) Radio stopped - (A1) Downlink radio stopped - (A3) Radio busy - (A4) Listen before talk - (A5) Radio board error - (A6) Specific failure cause for Semtech basics station packet forwarder Received too late for RX2 - (B0) Too late for RX2 Duty Cycle (DC) or gateway constraint on RX2 - (D0) >Duty cycle constraint detected by LRR - (DA) Duty cycle constraint detected by LRC - (DB) Max dwell time constraint detected by the LRC - (DE) DC not allowed by the peering operator (only applicable for passive roaming traffic) - (DF) Wrong NetID (i.e. device's NetID does not match the NetID associated with any eligible base station) |
| Over the air delivery error causes for RX2 downlink slot (class C devices only) | Class C device - Frame expired before transmission - (E0) Max delay for Class C (60 seconds), i.e. the class C packet could not be sent by the network due to timeout. |
| Over-the-air delivery error causes for downlink pingslots (class B devices only) | Transmission slot busy on ping slot - (A0) Radio stopped - (A1) Downlink radio stopped - (A2) Pingslot not available (i.e. no free pingslot found after several attempts over two beacon periods) - (A3) Radio busy - (A4) Listen before talk - (A5) Radio board error Received too late for pingslot - (B0) Too late for pingslot Duty Cycle (DC) or gateway constraint on pingslot - (D0) >Duty cycle constraint detected by LRR - (D9) No eligible LRR found because all have been discarded by the LRC - (DA) Duty cycle constraint detected by LRC - (DB) Max dwell time constraint detected by the LRC - (DC) No GPS-synchronized LRR detected by the LRC - (DD) No LRR connected detected by the LRC - (DF) Wrong NetID (i.e. device's NetID does not match the NetID associated with any eligible base station) |
Downlink metadata columns
Metadata is a series of information related to the transmission or reception of each packet. It allows you to monitor the radio conditions of each packet and the network-based MAC layer configurations.
The most important downlink metadata are directly displayed as distinct columns in Wireless Logger and are listed in the following table. For more information about other metadata displayed in the expandable panel of the packet, see Downlink expandable panel.
In the downlink packet content, ACK flag = 1 means that the downlink packet acknowledges the reception by the network of the last uplink packet.
This set of metadata also applies to multicast and passive roaming downlinks. For more information, see Downlink LoRaWAN® multicast packets and Passive roaming LoRaWAN® packets.
| Metadata | Description |
|---|---|
| Message direction | Red icons show the downlink packet (from the LRC to the device). |
| Message type | data indicates that the packet contains some applicative payload sent by the application server to the device (e.g. configuration message, actuator command etc.). mac indicates that the packet contains some MAC layer service commands (ADR modification and so forth…). join indicates the Join Accept message (for OTAA devices). See Downlink packets for more details. |
| UTC Timestamp | UTC timestamp, using ISO 8601 format. |
| Local Timestamp | Timestamp translated to browser time zone, using ISO 8601 format. |
| DevAddr | Device address (4bytes). |
| DevEUI | Device EUI (8bytes) is a global end-device ID in IEEE EUI64 address space that uniquely identifies the end-device. If the network server acts as a forwarding network server (fNS) and the message type is data, the DevEUI is only available if LoRaWAN® Backend Interfaces version > 1.0. |
| FPort | Application port of the packet. |
| NFCnt | Downlink frame counter maintained by the LRC network server. - For LoRaWAN® 1.0.x: NFCnt is filled with the downlink frame counter (always present). - For LoRaWAN® 1.1: NFCnt is filled with NFCntDown value (can be empty if the downlink packet contains application payload). |
| AFCnt | Downlink frame counter maintained by the application server. - For LoRaWAN® 1.0.x: always empty. - For LoRaWAN® 1.1: AFCnt is filled with AFCntDown value (can be empty if the downlink frame does not contain application payload). |
| SF/DR | Spreading Factor or Data Rate of the downlink packet. |
| Sub Band | Radio frequency sub band corresponding to the logical channel used to transmit the downlink packet to the device. |
| Channel | Logical Channel used to transmit the downlink packet by the device. Note The following color legend applies to downlink packets: - When the downlink packet is sent over RX1 slot, the LC-ID is displayed over white background. - When the downlink packet is sent over RX2 slot, the LC-ID is displayed over orange background. - When the downlink packet is sent over a class B pingslot, the LC-ID is displayed over blue background. |
| LRC Id | Identifier of the LRC network server. |
| Relay Id | DevEUI of the relay that forwarded the downlink packet to the end-device. |
| LRR Id | ID of the best-LRR sending the downlink packet to the device. For roaming-out use case (sNS passive roaming), the LRR Id corresponds to the identity of the best foreign gateway if this Id has been reported by fNS, otherwise a virtual LRR Id is displayed in Wireless Logger. |
Downlink expandable panel
The following elements are displayed in the expandable panel for each
LoRaWAN® downlink packet. To access the expandable panel, click
on the left side of the packet.
This set of metadata also applies to multicast and passive roaming downlinks. For more information, see Downlink LoRaWAN® multicast packets and Passive roaming LoRaWAN® packets.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Mtype | Indicates the type of packet: ConfirmedDataDown, UnConfirmedDataDown, JoinAccept: - Join Accept is sent by the LoRaWAN® Join Server to grant access to OTAA devices. It allows the device to derive the session keys and acquire the mandatory radio frequency parameters configured in the network. It is displayed in Wireless Logger with the Note The content of the Join Accept message is displayed in encrypted format by Wireless Logger. - If the downlink packet requires an acknowledgment by the device, it is sent in CONFIRMED mode. In this case, Wireless Logger displays the message type (Mtype) as ConfirmedDataDown. - Otherwise, downlink packets can be sent in UNCONFIRMED mode, meaning that the device is not requested to send back any acknowledgment to the network on its downlink data. This corresponds to the UnconfirmedDataDown message type. |
| Flags | MAC layer flags available in the Frame Header (for more details, see LoRaWAN® 1.0.3 MAC Layer specification): - ADR: always set to 1 if the command LinkADRReq is supported in the device profile of the device. - ACK: set to 1 if the packet contains an acknowledgement to the previous uplink packet, 0 otherwise. - ADRACKReq: not relevant for downlink packets. - FPending: set by the network to inform the device that other downlink packets are waiting for transmission on the network side. |
| MAC (hex) | Contains the downlink MAC commands in hexadecimal format, followed by the decoded content of each MAC command. |
| Data (hex) | Contains the downlink application payload in hexadecimal format. Note This payload may be hidden for sake of confidentiality. To learn more, see Displaying decoded data payloads. The payload encryption status (encrypted vs. not encrypted) is displayed between square brackets. |
| Driver metadata | Metadata associated with the device profile corresponding to the device in question. This metadata allows Wireless Logger application to automatically map the device to the right payload decoder from the list of IoT Flow drivers. For more details, see Displaying decoded data payloads. |
| Decoded data | Decoded applicative payload, available only when a valid payload driver exists for this device model and Wireless Logger decoder is not set to "no decoding". For more information, see Displaying decoded data payloads. |
| Data size (bytes) | Size of the applicative payload in bytes. |
| AirTime (s) | Time duration of the packet over the air (in seconds). |
| Delivery Status | Transmission status of the downlink packet by the LRR base station: - Sent: the downlink packet was successfully sent by the LRR. Note: Successful transmission by the LRR does not guarantee successful reception by the device, due to potential loss of the packet over the air (collision, link budget issues…). - Failed: the downlink packet could not be sent by the LRR over the air interface. The delivery failure cause on RX1/RX2/Pingslot (the latter is exclusive to class B devices) is provided in the expandable panel. For more information, see Downlink delivery failure causes. |
| ISM Band | LoRaWAN® ISM band (also known as regional profile as per LoRaWAN Regional Parameters specification) associated with the device and its best-LRR (BestLRR or BestGWID). |
| RF Region | RF region of the best base station (BestLRR or BestGWID). |
| AS ID | ThingPark ID of the application server sending the downlink packet to the device. This information is only applicable to downlink packets carrying applicative payload, otherwise the field is empty. |
| Frequency | Physical frequency (in MHz) used by the network to transmit the downlink packet. The corresponding Logical Channel is displayed in the Channel column. |
| Reporting status of the "Downlink Sent Indication" to AS | For each downlink packet requested by the application server (AS), the network sends back to AS a "Downlink Sent Indication" report describing whether the transmission has been successfully completed by the network's base station(s). When the interface between ThingPark the third-party application server uses Basic HTTP type of connections (also known as NS/AS tunnel interface), the transmission status of such "Downlink Sent Indication" report to AS is visible in Wireless Logger. Two possibles values are: OK or Error. In case of error, a message is displayed in the Transmission errors column. Note This status is only relevant for "Basic HTTP" type of connections. Delivery errors related to TPX connections are currently not visible in Wireless Logger. |
| Transmission errors | Applicable only if the transmission Status is Error. Idx: Index of the destination that caused the error. Starting value at 0. Url: The destination URL that returned the error. An HTTP Application Server can be configured with several destination URLs. Status: - Timeout: The report was not successfully acknowledged by the destination within the expected time frame. - Error: The report was rejected by the destination. (HTTP error, network error, DNS error). - Overload: The report was not sent to the destination because the network server reached the OVERLOAD state and the destination's average round trip time is too bad. - Blacklist: The report was not sent to the destination because the network server reached the BLACKLIST state and the destination's average round trip time is bad. - Unreachable: The report was not sent to the destination because this destination was deemed unreachable due to irresponsive behavior over the last observation window. Note This information is only relevant for "Basic HTTP" type of connections. Delivery errors related to TPX connections are currently not visible in Wireless Logger. |
| Confirmed network frame counter up (ConfFCntUp) | Only valid for LoRaWAN® 1.1 devices when the downlink packet acknowledges the last uplink packet sent in confirmed mode. It indicates the uplink frame counter FCntUp being confirmed by the LRC (ACK sent by the LRC).This field is visible in the downlink expandable panel. |
| Transmission slot | Either RX1, RX2, Pingslot or RXR (the latter is valid only for downlink packets forwarded via a LoRaWAN relay). Note "RXR (repetition)" means that the transmission of the downlink packet was attempted twice by the network: via a direct base station (using conventional RX1/RX2 slots) and via a relay (using RXR slot). This DL repetition helps maximizing the device's chances to successfully receive the downlink packet when it is in the coverage border between a conventional base station and a relay. |