Reference information
Licensing modes
ThingPark Network Coverage tool supports two types of licensing:
- Credit-based license, as described in Credits
- Time-based license, allowing you to run unlimited number of simulations until the expiration date
is reached.
To purchase time-based licenses, contact your Actility sales representative.
Credits
In credit-based license mode, you need to have credits to be allowed to launch new simulations. 1 credit corresponds to the coverage simulation of 1 base station. For instance, if you have 2 credit points left, you can either launch 2 simulations of 1 base station each, or 1 simulation with 2 base stations.
Each base station given as input in the simulation scope counts "1" in your credit verification, whether the Smart Antenna Selection feature is activated to optimize the candidate base station list, or not. A base station deactivated after an optimized simulation still counts as 1 credit.
The top-right corner of the user interface displays 2 types of credits:
- Remaining free credit
- Remaining purchased credit.
Each credit is expressed as XX/YY, where XX is the credit available to date and YY is the total credit originally available.
By default, you get 5 free credit points every 90 days. The date of free credit refuel is displayed by hovering your mouse on this field.
You can purchase extra credits through the ThingPark Market. The extra credit purchased can be used at any time, without any validity deadline. The current status of our paid credit is also displayed in the top right corner of the user interface.
When launching a new simulation, free credit is debited first then purchased credit next. A simulation cannot run if the sum of remaining free + purchased credits is not enough.
If a simulation fails, the credit points used for the simulation (free and/or purchased credits) are restored in the same way they were originally debited.
Device location
There are 4 possible device locations in the tool:
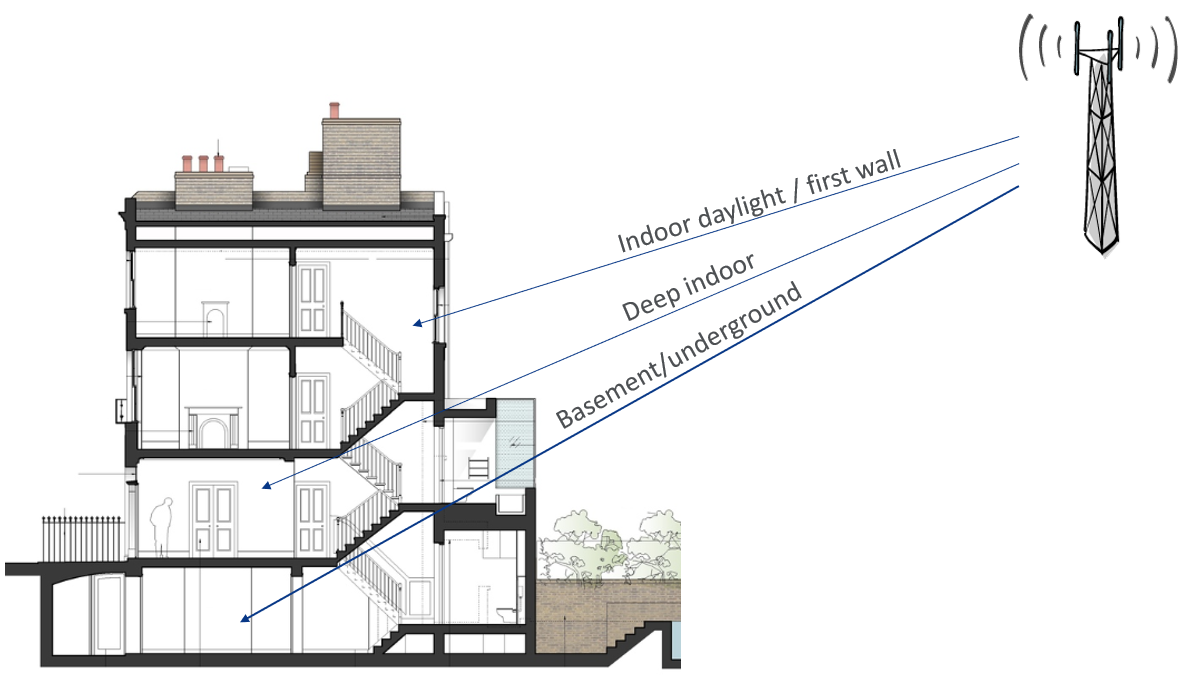
- Outdoor: devices are located outside buildings.
- Indoor daylight: devices are located inside buildings but near a window or with only 1 wall between the devices and the outdoor base stations, e.g. close to the building facade.
- Deep indoor: devices are located inside buildings with several walls between the devices and the outdoor base stations, i.e. deep inside the building.
- Basement: devices are located inside buildings, in a basement or very difficult-to-reach areas, e.g. underground or in a very deep indoor location inside a building, with metallic barriers.
CSV file for BS list
The CSV input file must contain the following information per base station :
- LRR-ID: this is a free-text field, you can set the base station ID or its name.
- Latitude: LoRa antenna latitude in decimal degrees.
- Longitude: LoRa antenna longitude in decimal degrees.
- Height above ground: LoRa antenna height above ground in meters.
- Propagation environment: see Propagation environments.
- Antenna pattern: you can see the list the supported antenna patterns in the Antenna Pattern page of the user interface. The Antenna_pattern column must be filled with the antenna name as written in the Antenna Pattern tab.
- Cable losses: total cable losses between the base station and the LoRa antenna, in dB.
- Forced activation: if the Smart Antenna Selection feature is activated and if this parameter is set to 1, the gateway will be selected in the simulation results.
CSV file for device dataset
You can create a device dataset by importing a CSV file. The CSV input file must contain the following information per device :
- Name: this is a free-text field, you can set the device ID or its name.
- Latitude: device latitude in decimal degrees.
- Longitude: device longitude in decimal degrees.
- Location: outdoor, indoor daylight, deep indoor, basement. If this parameter is not filled, the default device location set in the simulation form is applied for the device.
Propagation environments
There are 4 propagation environments available :
- Dense Urban: High building density with more than 6 floors per building, typically in the city center or business districts. Buildings are separated by narrow streets with very limited vegetation.
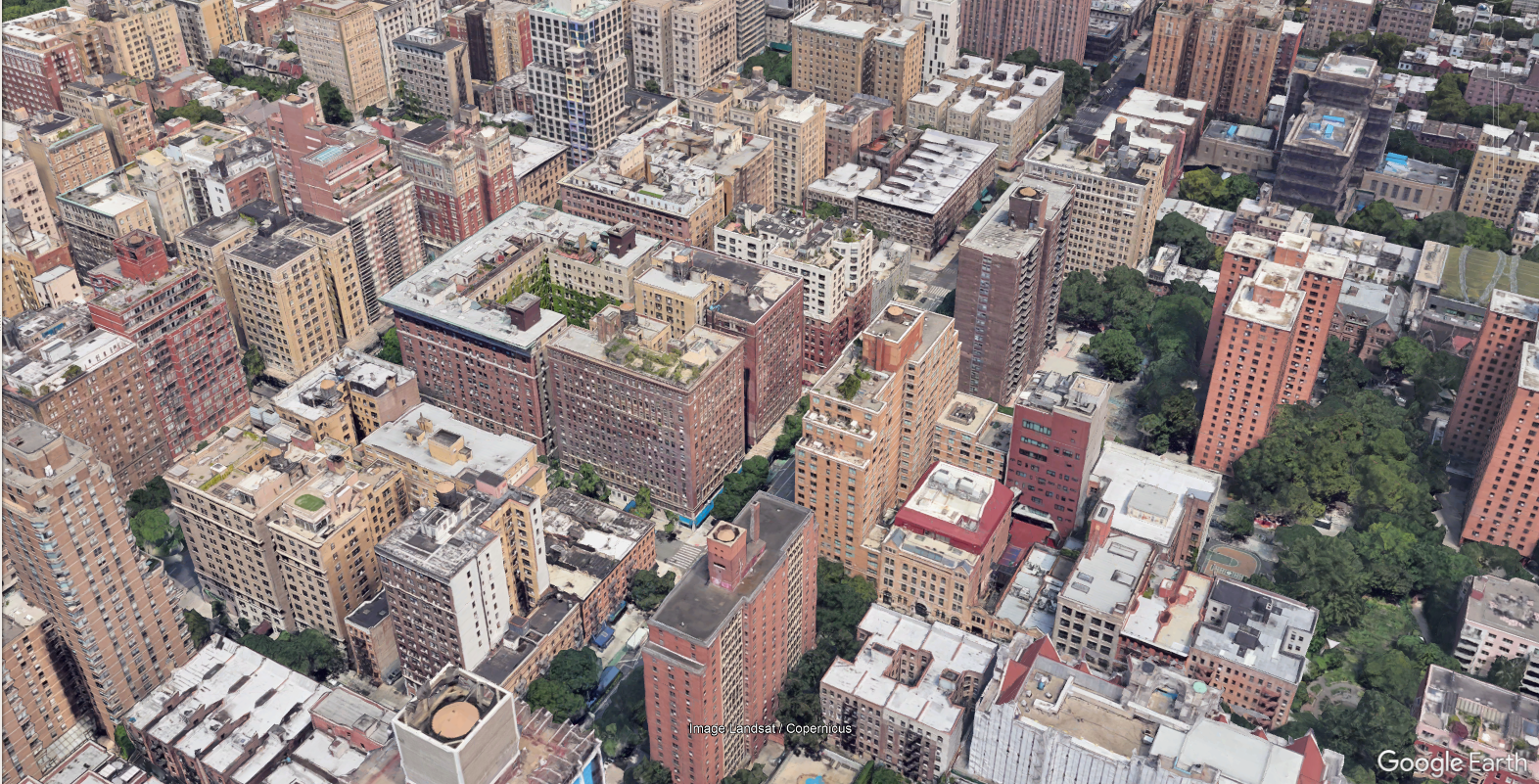
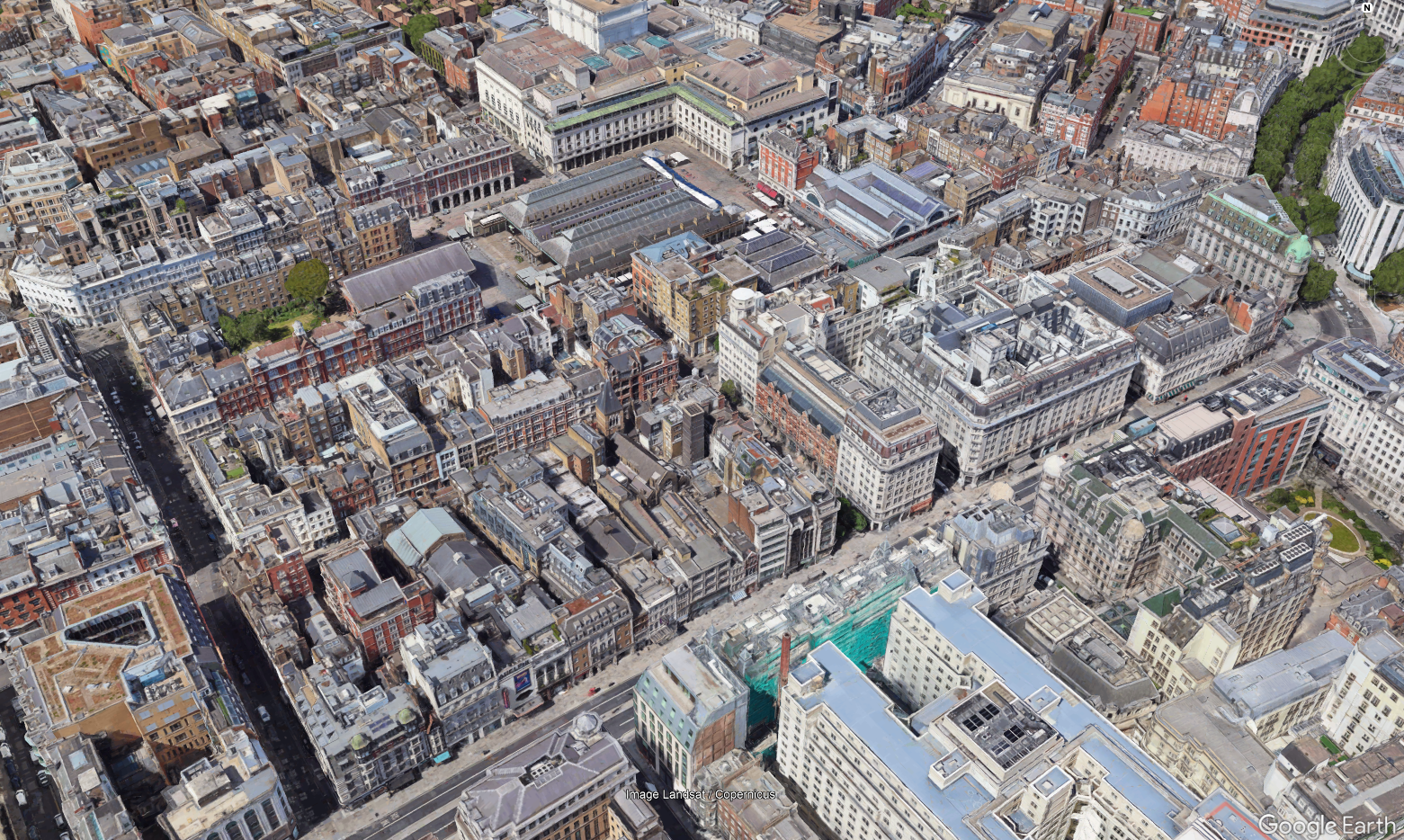

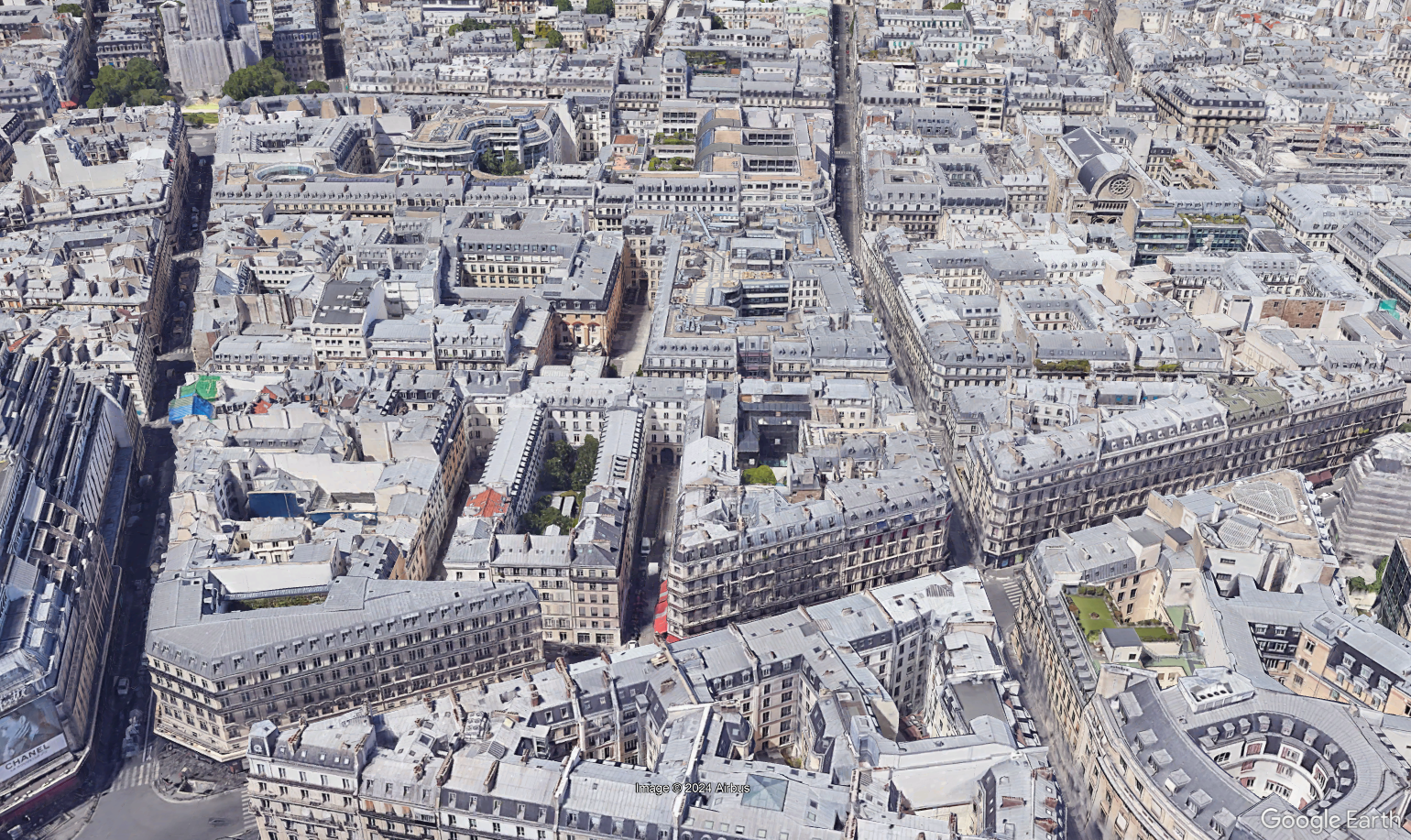

- Urban: High density of 4-6 floors buildings, generally located in or near the city centers. Buildings are separated by larger streets than dense urban, but the vegetation is still rather limited.
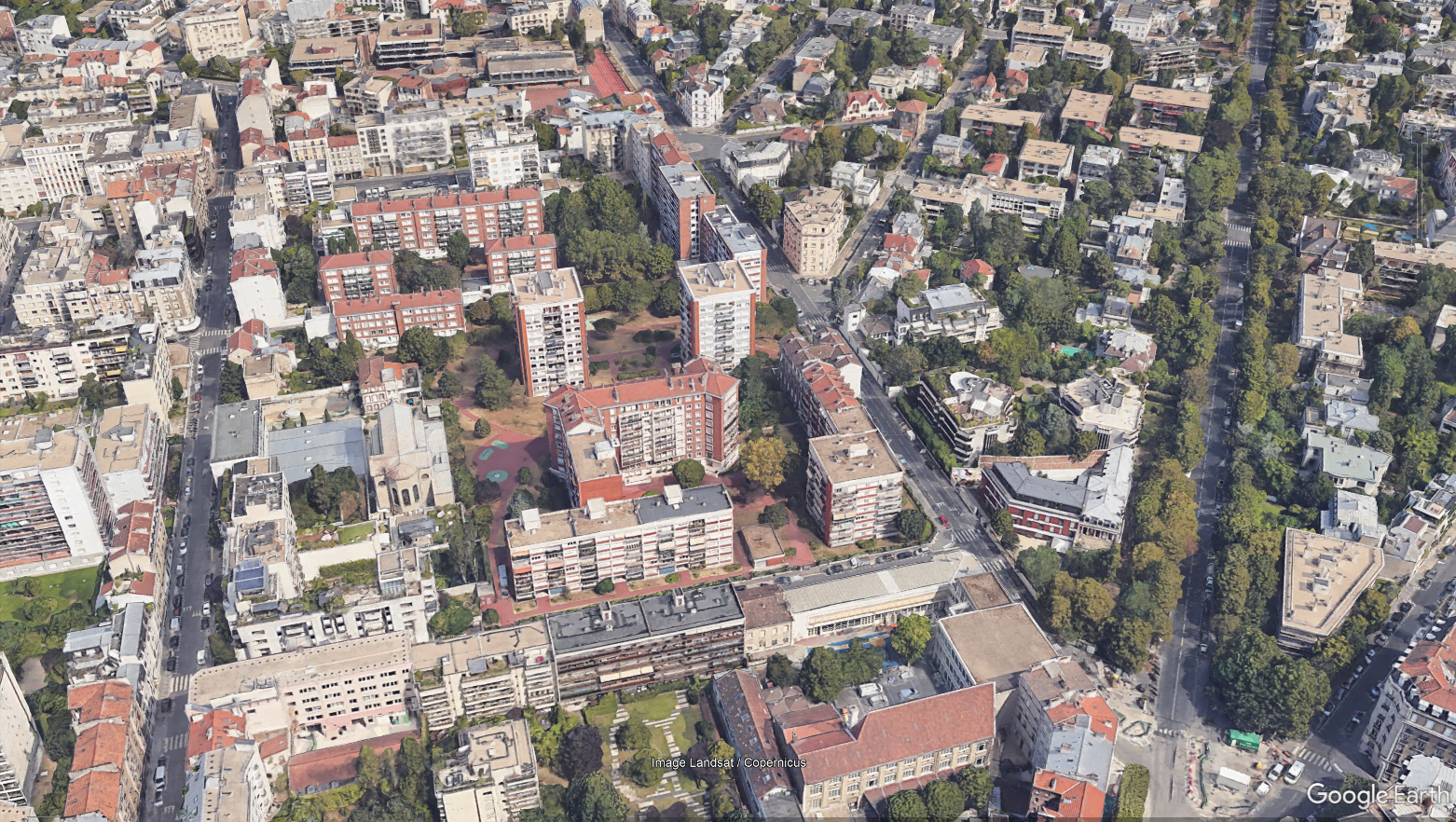
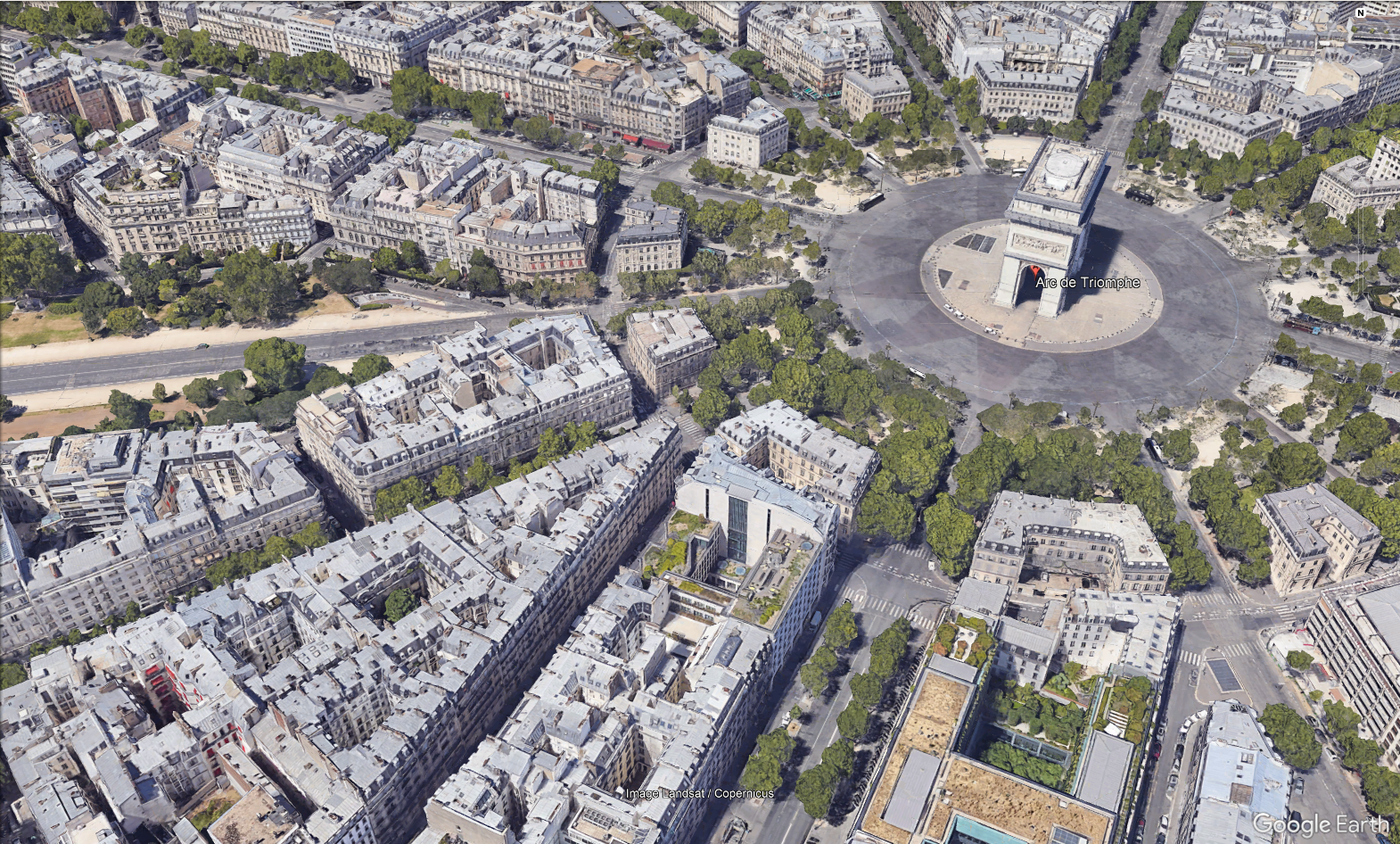



-
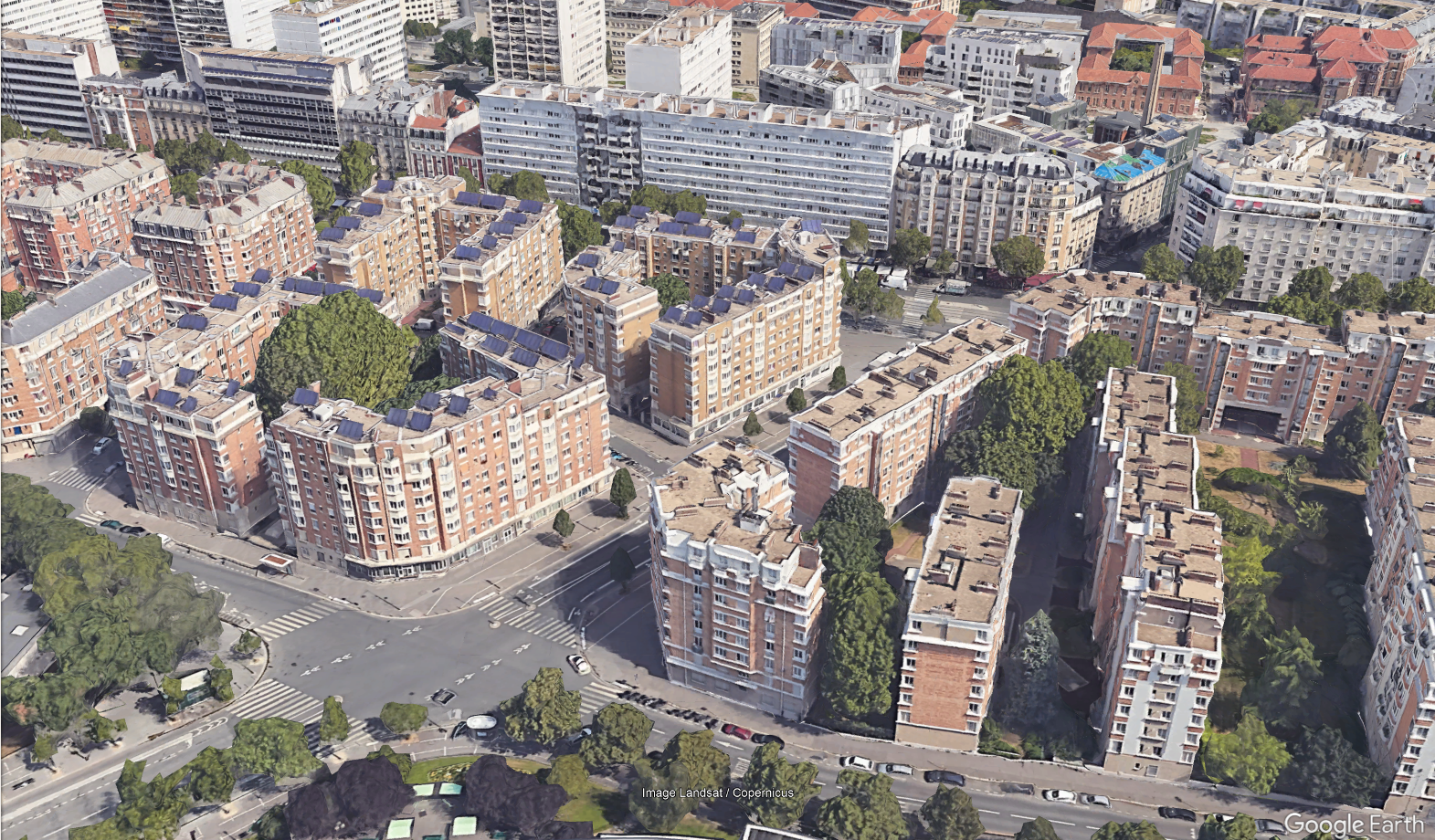
Suburban:
- 2-4 floors buildings close together, or blocks of 2-3 buildings separated by
large streets

- Industrial zones: Factories, warehouses, garages, shopping centers, airports
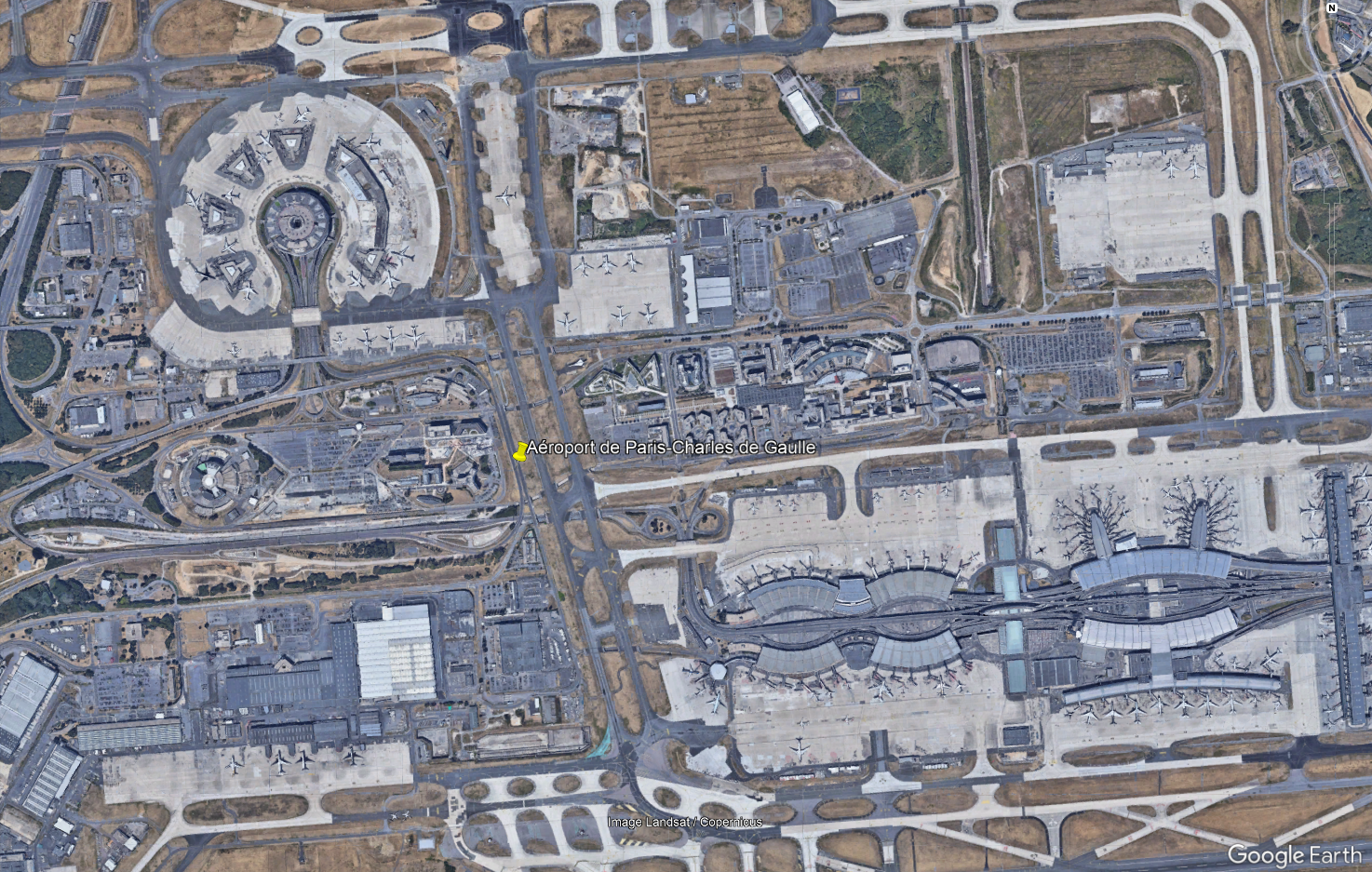

- Residential areas: 1-2 floors houses with garden surrounding cities
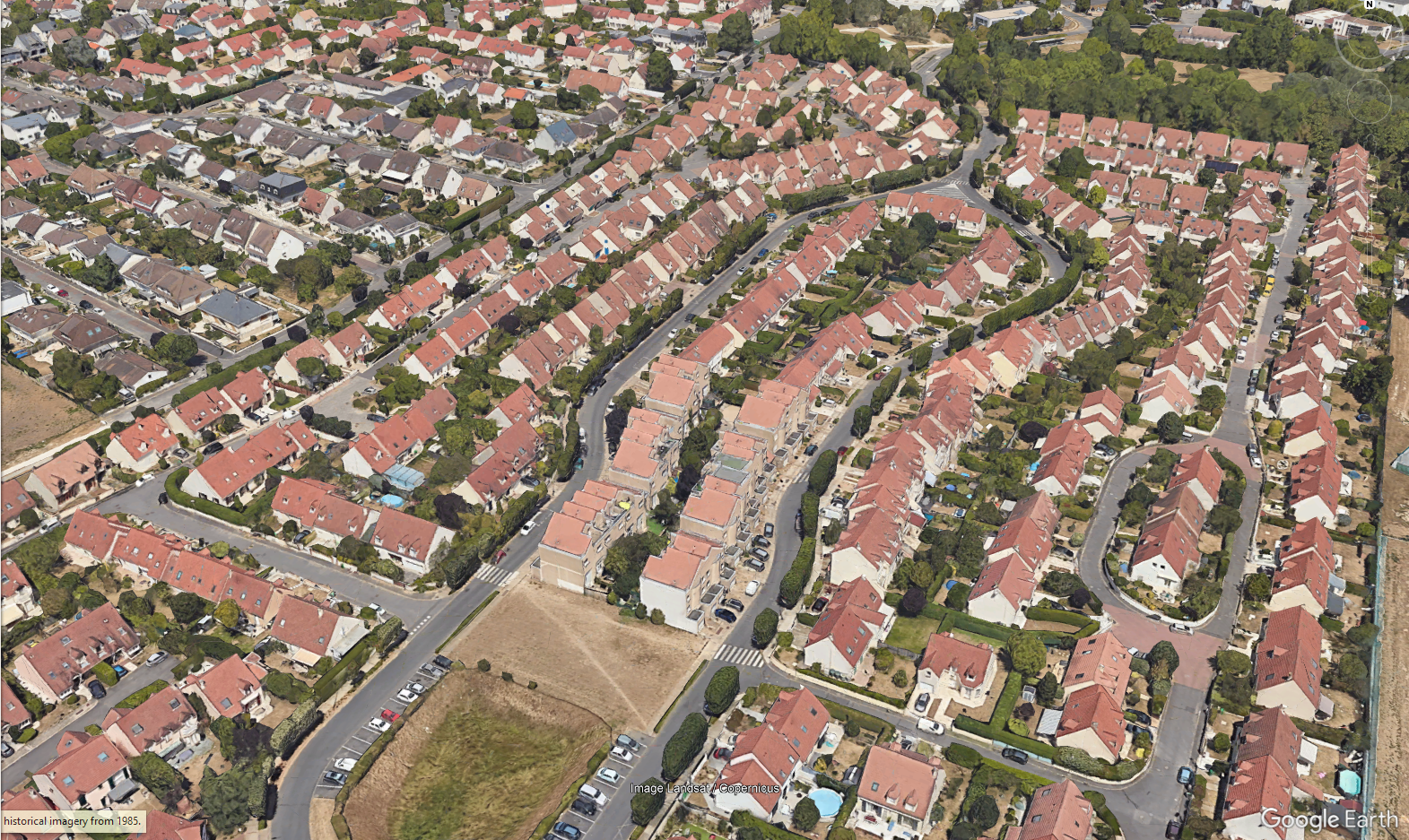

- 2-4 floors buildings close together, or blocks of 2-3 buildings separated by
large streets
-
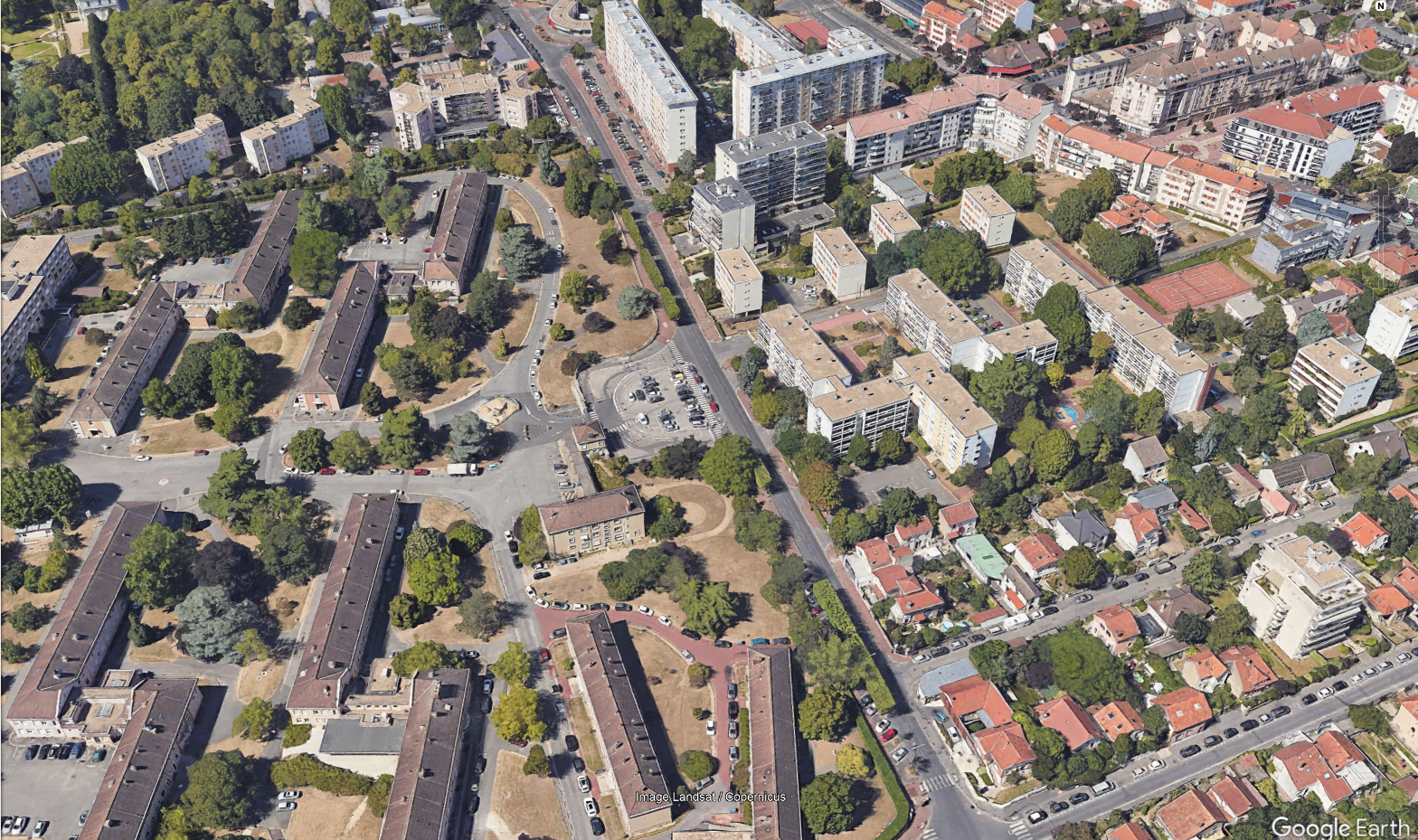
Rural:
- Wide area with scattered houses and a lot of agriculture, forests...
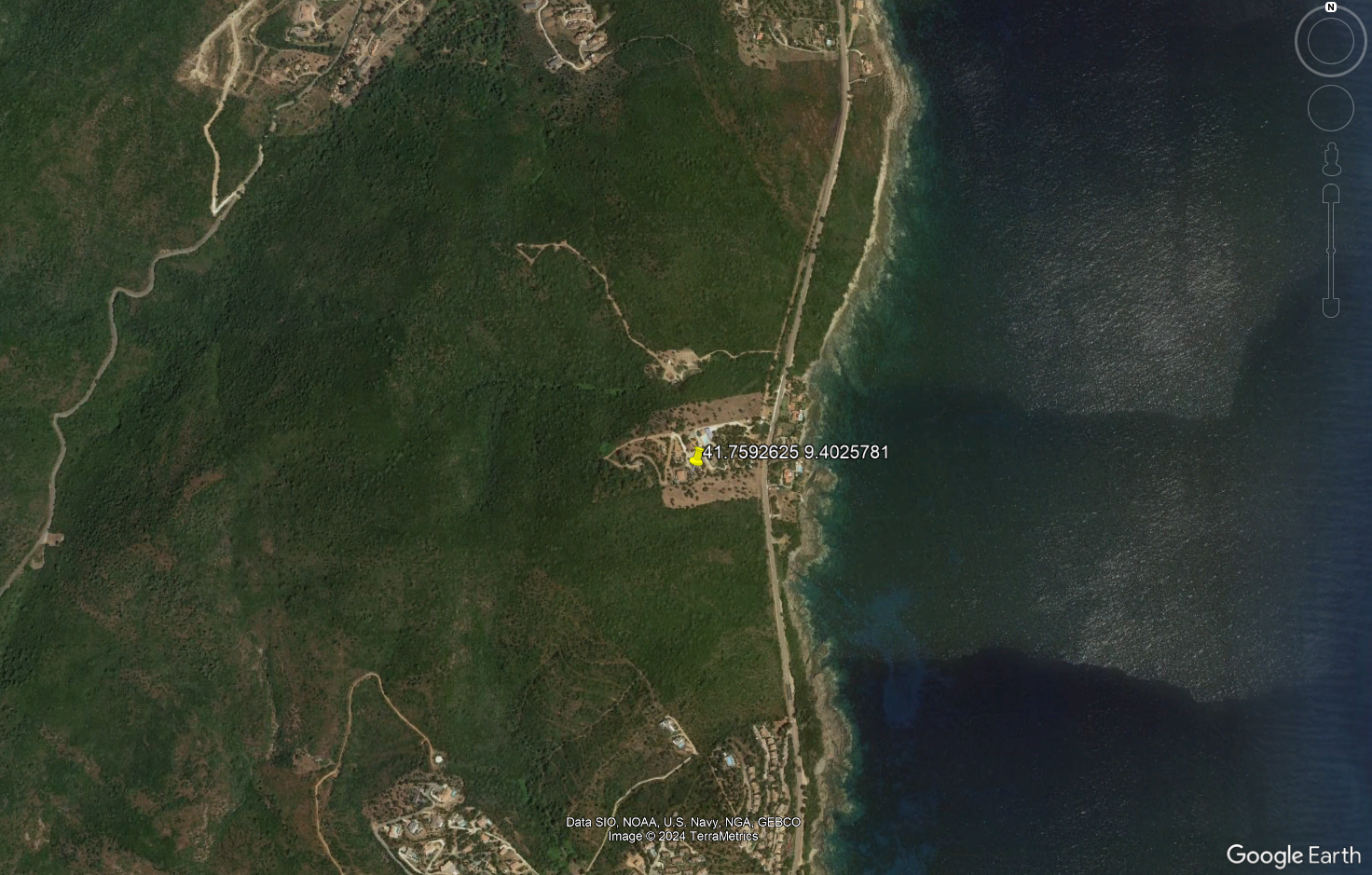
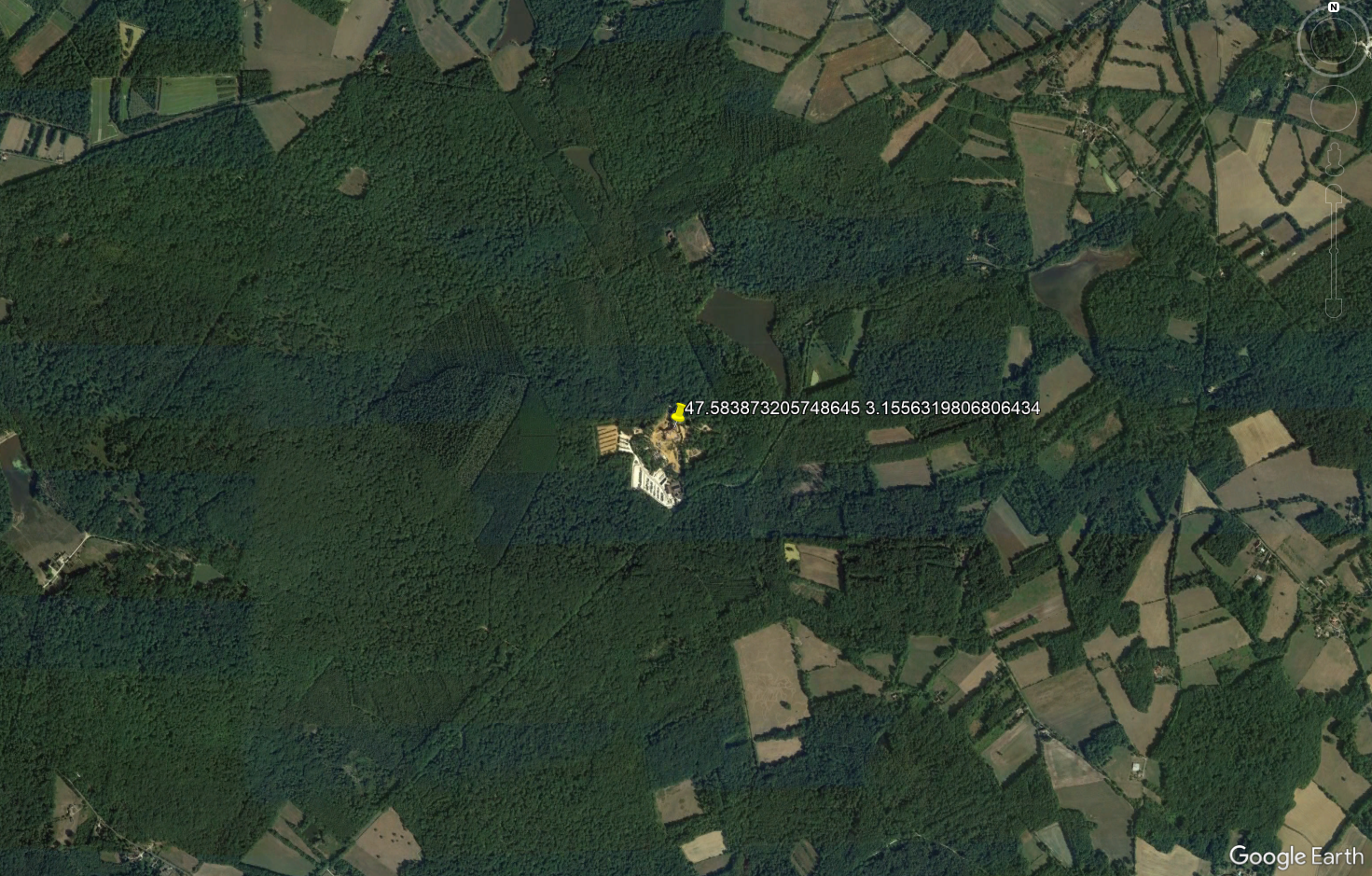
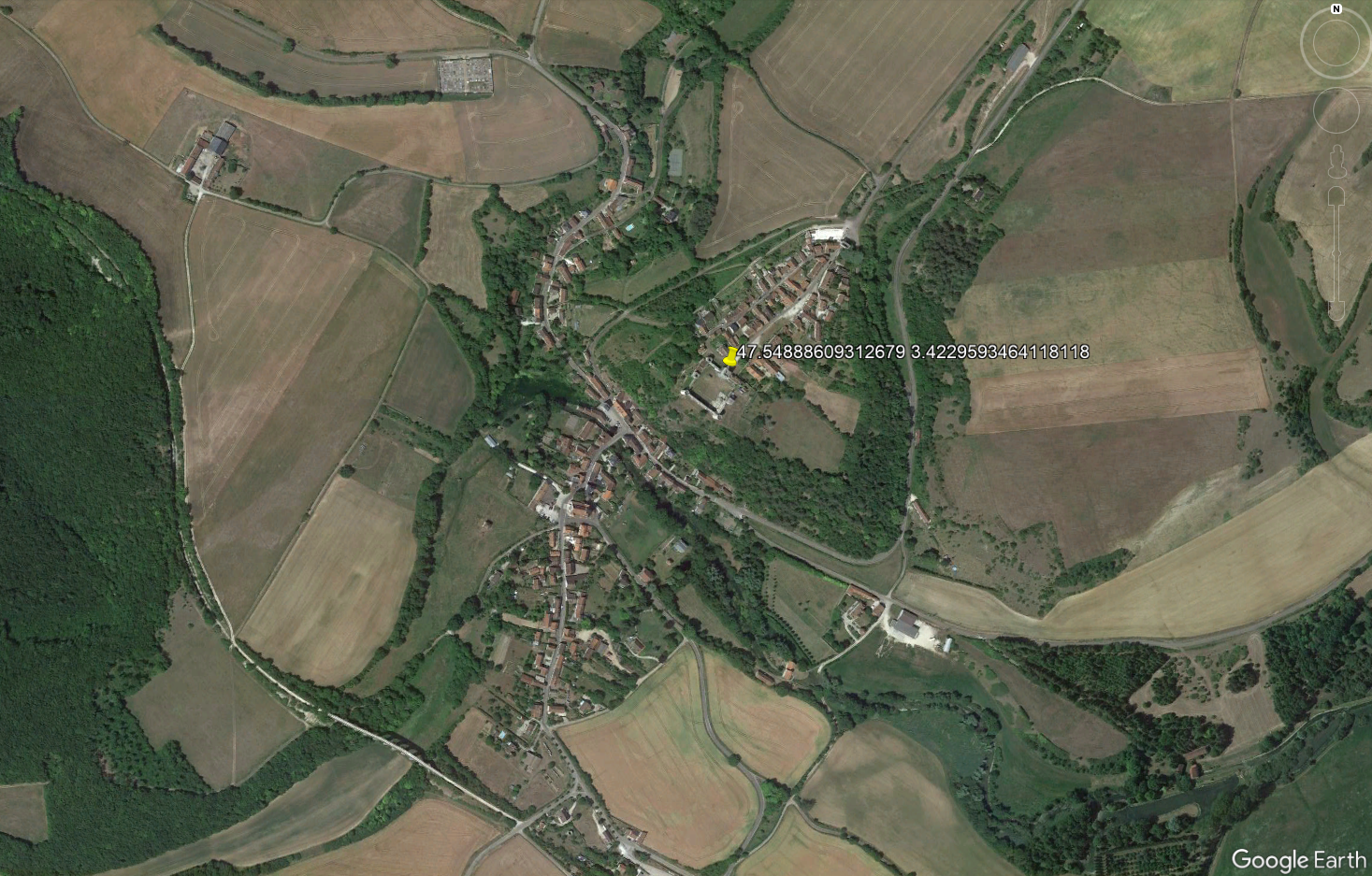
- Village: 1-2 floors houses in rural areas

- Wide area with scattered houses and a lot of agriculture, forests...