New features
This page cumulates all the new ThingPark Enterprise features brought by the different 8.0.x software releases. See the 8.0 changelog to know more about the split of those features per maintenance release.
The features described in this page are common to SaaS and Self-hosted ThingPark Enterprise products.
Enriched configuration of Basic HTTPS connections RDTP-11863
The following enhancements are added to basic HTTPS type of connections towards external application servers:
-
Each connection may be configured with several destination URLs. When this is the case, the routing strategy can be defined as one of the following options:
- Sequential: The packet is transmitted to the first destination of the ordered list, then it is attempted on the following URLs only in case of transmission failure on the preceding URL of the ordered list.
- Blast: each uplink packet is sent to all the destination URLs.
-
Support port-based routing, allowing to route uplink traffic according to the LoRaWAN
Fportincluded in the uplink packet. This feature offers segregated routing/processing of the LoRaWAN traffic by multiple applications. -
The maximum timestamp deviation for tunnel interface authentication now is configurable in the user interface. This parameter defines the maximum allowed deviation between the timestamp set by the application when the downlink request is generated, and the time of reception of the downlink request by the network server.
-
The URL used to send downlink packets to this connection is now displayed in the detailed page of each basic HTTPS connection.
More details
Key customer benefits
Enhanced user experience + additional flexibility using HTTPS connections.
Feature activation
This feature is automatically available after the upgrade to release 8.0.
HTTPS connections created from previous releases remain unchanged after the upgrade. It is up to the Connection manager to manually edit the connection details if they want to add several destinations or support port-based routing.
Feature limitations
Not applicable.
Improved monitoring of the device's battery history RDTP-17339
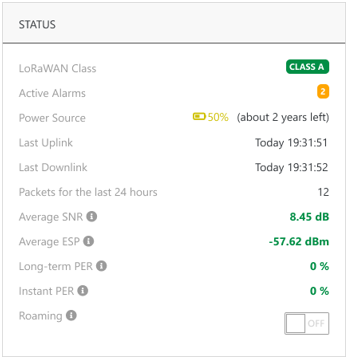
Prior to release 8.0: the user interface displays only the last reported battery level for each LoRaWAN device.
Starting release 8.0: in addition to the last reported battery level, the following information is available in the user interface, for battery-powered LoRaWAN devices:
-
The estimated delay until the battery should be recharged/replaced.
-
The date when the battery was recharged/replaced.
-
The battery usage history graphs over the last 3 months, 6 months and 1 year.
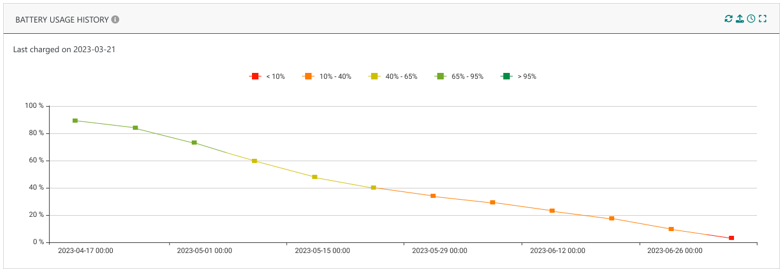
More details
Key customer benefits
Improved monitoring of battery-powered devices, including the ability to estimate the remaining battery lifetime by extrapolating the history of reported battery levels.
Feature activation
This feature is automatically available after upgrading to release 8.0.
Feature limitations
Not applicable.
Device management UI/UX enhancements RDTP-16304
Release 8.0 brings the following UI/UX enhancements regarding the device management aspects:
-
Adding devices without connections: It is now possible to add new devices or multicast groups without associating them with any Connection.
-
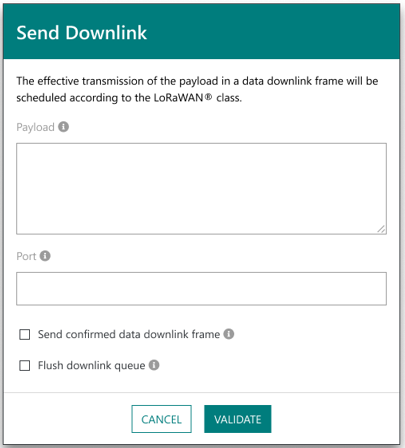
Enhancements related to sending downlink packets: It is now possible to send encrypted downlink payloads, which is relevant for devices configured with the end-to-end encryption mode and AppSKey is only known to the Application Server. In this case, the downlink frame counter must be entered by the user in addition to the encrypted payload and the frame port.
Additionally, the "Send downlink" feature is enhanced to allow sending downlink packets in confirmed mode (that is to say, requesting an acknowledgement from the device) as well as flushing the downlink queue for class A devices.
-
Multicast groups: AppSKey is now optional when adding new multicast groups.
More details
Key customer benefits
Enhanced user experience and improved operational efficiency:
-
Test devices may be added to the system without associating them with any connection. This enhancement removes the need to create a dummy connection if the device is temporarily dissociated from all the real connections.
-
Additional options are now supported when users send downlink packets through the user interface.
Feature activation
This feature is automatically available after the upgrade to release 8.0.
Feature limitations
It is currently not possible to send encrypted downlink payloads to a multicast group created without AppSKey.
Allow managing domains, user accounts and service accounts through API RDTP-19650
Prior to release 8.0: managing domains, user accounts and service accounts is only possible through the user interface.
Starting release 8.0: besides the user interface, it is now
possible to manage domains, user accounts and service accounts
through the OSS API.
To learn more about the new API, see Subscriber administration.
More details
Key customer benefits
This feature offers the following benefits to ThingPark Enterprise administrators:
- Better integration with the customer's business applications.
- Better experience, allowing bulk management through API scripts.
Feature activation
This feature is automatically available after upgrading to release 8.0.
Feature limitations
Not applicable.
Use of distroless containers RDTP-22478
Distroless containers are a minimalist approach to building Docker containers, where only the essential files required to run an application are included. This contrasts with traditional containers that often include a full Linux distribution with many extra packages and utilities.
More details
Key customer benefits
Using distroless containers offers a wide range of benefits:
-
Improved security: with fewer components and libraries, the attack surface of the container is drastically reduced, limiting the potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. This improves security as there are fewer opportunities for vulnerabilities within the image, reducing the risk of malicious code being injected or security breaches. Since there are fewer components, there’s less to maintain or update in the container, and fewer packages needing to be patched for security vulnerabilities.
-
Smaller image size, by removing unnecessary libraries, binaries, and tools found in a full Linux distribution. This means faster pull and push times, reduced storage needs, and more efficient use of bandwidth.
-
Performance optimization: by stripping down everything except what is needed for the application, resource consumption is minimized. Hence, containers become more efficient, requiring less memory and CPU and offering faster startup times.
Feature activation
This feature is automatically available in ThingPark 8.0.
Feature limitations
In release 8.0, applications that could not use distroless mode for whatever technical constraints use the debian-slim mode instead, which is still better than the traditional container mode.
LRR support password personalization from the GUI RDTP-22321
Prior to release 8.0:
-
The default password of the LRR support account can only be changed from the local console (also known as Suplog), for LRR version 2.8.39 onwards.
-
If the support password is changed locally via Suplog, the user is asked to enter its new password every time they want to open a remote session to the LRR from the ThingPark user interface.
Starting release 8.0:
-
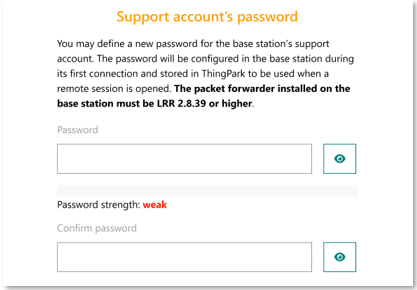
The BS manager may personalize the support password during the BS provisioning step on the user interface:
-
Additionally, the BS manager may change the current support password at any time, either by API or from the Advanced tab of the base station's detailed page:
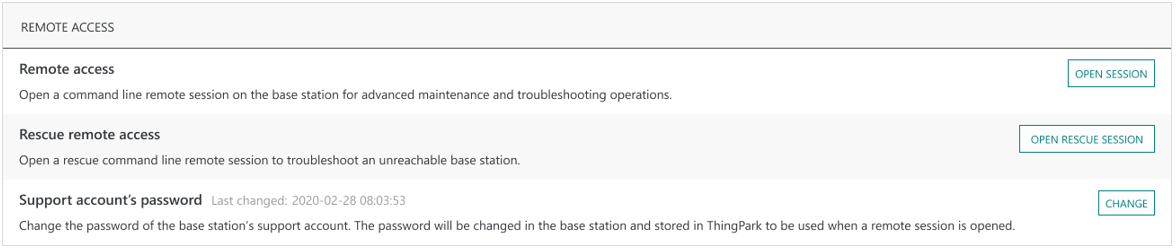
-
Whenever the password is changed from the BS management interface (or by API), the new password is automatically stored by the back-office so that the user is not requested to enter it again every time a new remote session is initiated.
More details
Key customer benefits
Besides the security enhancement brought by the ability to personalize the default password of the LRR support account, this feature brings operational gains to ThingPark base station managers:
- Users may change passwords in bulk for all their base stations, through API scripts.
- The personalized password is memorized by the system, enhancing the overall user experience during remote access.
Feature activation
This feature is automatically supported for base stations running the LRR packet forwarder with starting version 2.8.39. It is not supported for base stations running Basics Station packet forwarder.
Feature limitations
When restoring an LRR backup, the support password in use at the time of the backup is restored. In this case, the password stored on the server may be no longer valid and must be manually entered by the user when opening a remote session from the user interface.
Flapping mitigation of base station alarms RDTP-18707
To minimize volatility and reduce flapping occurrences, the implementation of base station alarms has been totally reworked in release 8.0.
Base station connection status (alarm #102):
To improve its relevance and mitigate flapping occurrence due to micro disconnections, both trigger and clearing conditions have been enhanced in ThingPark 8.0 as follows:
-
The alarm is raised only if the backhaul connection is interrupted for at least X seconds (X being configurable at base station level, it is set to 30 seconds by default). Additionally, the alarm severity is configurable (set to critical by default).
-
The alarm is cleared only when the backhaul connection is reestablished and stable for at least 10 minutes.
The trigger and clearing conditions of other BS alarms have also been reworked, either to extand the observation window or to increase the hysteresis, as detailed below:
More details
Unusually high level of invalid uplink physical CRC (alarm #104):
- The trigger condition is improved by evaluating the ratio of CRC errors over 4 consecutive hours instead of only one hour.
- The clearing condition is also improved by evaluating the CRC error ratio over 4 hours while considering 20% hysteresis instead of 10%.
Downlink frame rate exceeds the RF cell capacity (alarm #105)
- The trigger condition is improved to raise the alarm when the ratio of DL dropped frames (due to busy radio modem) exceeds 5% over the last hour; instead of previously raising the alarm upon the first dropped DL packet.
- The clearing condition is also improved: the alarm is cleared when the DL dropped packet ratio gets below 2% over the last hour.
Unusually high CPU usage level (alarm #106)
- For simplification, the "warning" severity is removed, only one severity level (major by default) is kept.
- The alarm is raised when the average CPU usage (evaluated over the last hour) exceeds 90%, as opposed to evaluating the CPU usage every 5 minutes in previous releases.
- The alarm is cleared when the average CPU usage (also evaluated over the last hour) gets below 80%, providing 10% hysteresis.
Unusually high RAM usage level (alarm #107)
- For simplification, the "warning" severity is removed, only one severity level (major by default) is kept.
- The alarm is raised when the average RAM usage (evaluated over the last hour) exceeds 90%, as opposed to evaluating the RAM usage every 5 minutes in previous releases.
- The alarm is cleared when the average RAM usage (also evaluated over the last hour) gets below 75%, providing 15% hysteresis.
Unusually high file system usage level (alarm #107)
- For simplification, the "warning" severity is removed, only one severity level (major by default) is kept.
- The alarm is raised when the average file system usage (evaluated over the last hour) exceeds 95%, as opposed to evaluating the file system usage every 5 minutes in previous releases.
- The alarm is cleared when the average file system usage (also evaluated over the last hour) gets below 85%, providing 10% hysteresis.
Time synchronization lost (alarm #109)
- The trigger and clearing conditions are improved by evaluating the time synchronization status over the last 15 minutes instead of only the last 5 minutes in previous releases.
Power failure detected (alarm #110)
- The trigger and clearing conditions are improved by evaluating the power status over the last 15 minutes instead of only the last 5 minutes in previous releases.
Beacon transmission failure (alarm #111)
- The trigger condition is improved to raise the alarm when the ratio of beacon transmission failures exceeds 25% over the last hour; instead of previously raising the alarm upon delivery status of the last beacon.
- The clearing condition is also improved: the alarm is cleared when the DL beacon failure ratio gets below 10% over the last hour, providing 15% hysteresis.
Backhaul network interface status (alarm #121)
- The trigger and clearing conditions are improved by evaluating the interface status over the last 15 minutes instead of only the last 5 minutes in previous releases.
GPS lock failure detected (alarm #122)
- The trigger and clearing conditions are improved by evaluating the GPS status over the last 15 minutes instead of only the last 5 minutes in previous releases.
Key customer benefits
Thanks to this feature, base station alarms become more relevant to BS managers, reducing their volatility and flapping occurrences.
Feature activation
This feature is automatically activated. Depending on the alarm, default settings may be configurable at base station level (such as alarms #102 and #103) or operator-wide.
Feature limitations
Not applicable.